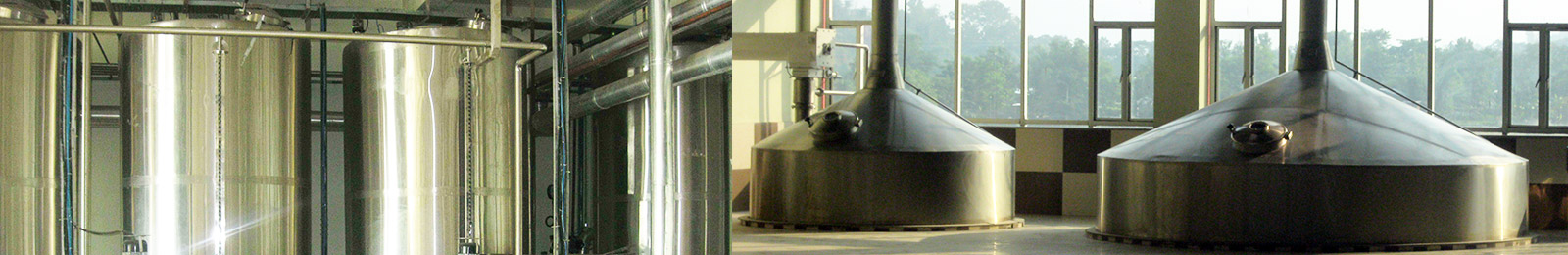
Brew House
Rice Cooker & Mash Kettle
Rice cooker & Mash Kettle consist of premasher, steam heating jacket on bottom cone & shell for Independent heating zones, VFD based Agitator at the bottom of the tank that facilitates mixing process with lower shear force and higher heat conductivity, CIP cleaning device, Insulated with the SS weld able cladding. The grist is mixed with water to form a mash which is carefully heated and agitated in the mash tun. Under controlled temperatures the natural enzymes begin converting the insoluble starches and proteins into a soluble malt extract known as the wort, which contains fermentable sugars including maltose.
Lauter Tun / Mash Filter
The term Lauter comes from the German word abläutern, meaning roughly “to rinse off” or purify. Lautering is a process in brewing beer, in which the mash is separated into the clear liquid wort and the residual grain. Lautering usually consists of 3 steps: mashout, recirculation, and sparging.
Only the wort is used for beer production. This separation process is called lautering or filtration depending on with what the mash separation is performed: either with a Lauter tun or a Mash filter. In a mash filter, the filtration occurs primarly through close-meshed filter cloths fixed on plates. This enables better recovery of the extract absorbed in the spent grains. Furthermore, through a large amount of filtration plates, a larger filtration’s area is created, which means as well a faster process.
Wort Kettle
Once the wort is separated from the husks, it is transferred to the wort kettle to be boiled. This process develops colour and flavour. Boiling helps extract the bitter and aroma substances from the hops, which are introduced at this stage together with the sugar.
The boiling also sterilises the wort and inactivates the malt enzymes, prior to the introduction of the yeast in the next stage.
Internal reboiler system uses a shell heat exchanger located inside the kettle. Wort is forced through the boiler mechanically. It’s designed to minimized shear force and less heat loss.
External wort boiler system : wort is heated through a shell and tube heat exchanger that located outside the kettle.
Hop dosing vessel is pressurized tank with The vessel is provided with wort inlet/outlet, CIP spray ball with CIP inlet, pressure relief valve, anti-vacuum valve, seal and safety switch.
ENERGY RECOVERY PLANT the Heat lost from the wort kettle is recovered and used to pre-heat future batches of wort with a vapor condenser on the exhaust stack.
- Reduces the need for steam
- Faster heat-up in the wort kettle based on heating the lauter wort from 72 °C to 92 °C
- less energy demand, lower operational costs, and faster brew times.
Whirlpool
After boiling, the wort is transferred to the whirlpool, here Wort enters the whirlpool in a tangential entry that creates the whirlpool motion. The whirlpool motion draws the trub out of the wort via centrifugal motion and forms a trub “cone” — a pile in the bottom center of the tank. Before moving on to fermentation, the hot wort is be cooled and prepared for the addition of yeast. Hot wort is transferred out of the whirlpool through a plate heat exchanger. This heat exchanger cools the wort very quickly, to about 10 0C, by running chilled water through pipes parallel to those holding the hot wort, as it is sent to the uni-tank for fermentation.
Clean-In-Place (CIP)
CIP systems developed as a means for reducing the amount of labor needed for cleaning and sanitizing operations. One of the main advantages of CIP systems is that they can recirculate and allow the reuse of chemicals and rinse water, thereby reducing consumption by as much as 40-50%.
CIP systems largely remove human contact with cleaning and sanitizing agents, thus reducing the risk of harmful exposure.
- Adopted Fully automated Centralized C.I.P Systems for hot & cold block.
- Hot Section : Water tank, Hot Caustic tank, Acid tank, Disinfection tank,
- Cold Section : Water tank, Cold Caustic tank, Acid tank, Disinfection tank
- With supply & return pumps, caustic dosing system, flow plates, cleaning turbines.
Brewing Liquor Tank
Water used for beer production-mashing, boiling, sparging, filtration, and packaging-breweries also use water for heating and cooling as well as cleaning and sanitation of equipment and process areas. Hot, Cold & Chilled water tanks, called liquor tanks in a brewery. These are buffer tanks that contain hot, cold & chilled water that will be used in various process of breweries.